Overcoming Affordability Challenges with Patient-Centered Solutions
Data and insights can drive affordable medication access for patients.

With many patients struggling under rising medication costs and affordability barriers, pharma manufacturers have an opportunity to create solutions for more patients to access their therapies. The right data and insights can help inform these efforts to create real-world solutions to affordability problems.
In this report, we discuss what’s preventing patients from affording their medications and how pharma manufacturers can respond.
The Affordability Landscape Today
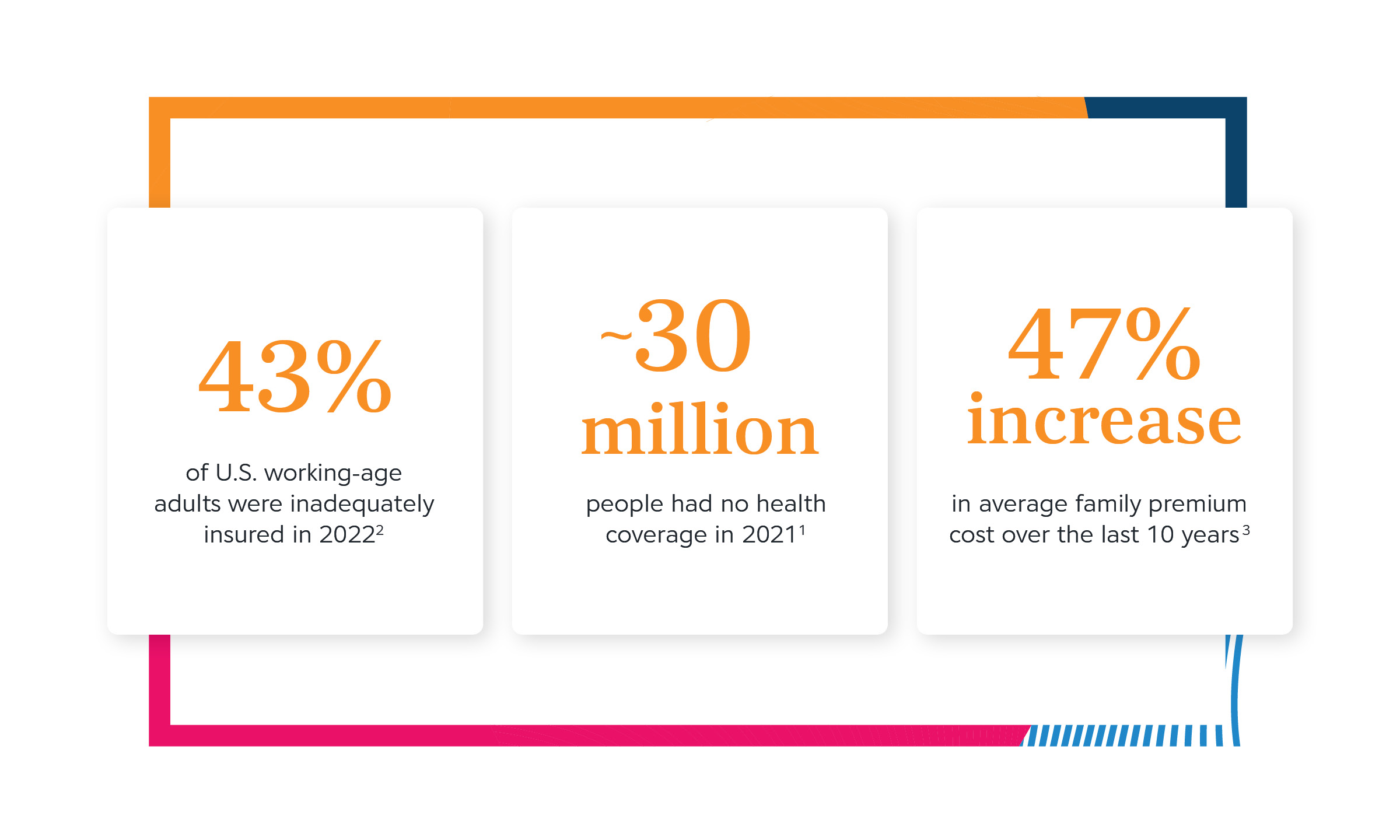
Too many patients in the U.S. can’t afford the medications they need. This presents a real problem for pharma manufacturers helping patients treat acute and chronic conditions.
Many patients are uninsured or underinsured — meaning many are exposed to the full costs of their medications and healthcare. In 2022, 27.4 million Americans were estimated as uninsured, representing 8.3% of the total population.Health Insurance Coverage: Early Release of Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, National Center for Health Statistics, January–June 2022 For adults 18-64, 12.1% were uninsured.Health Insurance Coverage: Early Release of Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, National Center for Health Statistics, January–June 2022 Even for patients with insurance, the rate of underinsured — those whose coverage is financially inadequate for their needs — is rising, most significantly among U.S. adults enrolled in employer-sponsored health plans.The State of U.S. Health Insurance in 2022, Commonwealth Fund, 2022 From January through June 2022, among people of all ages, 8.3% were uninsured, 39.2% had public coverage, and 61.4% had private coverage.Health Insurance Coverage: Early Release of Estimates from the National Health Interview Survey, National Center for Health Statistics, January–June 2022 The under- and uninsured are most likely to be fully exposed to their healthcare costs for a longer duration of the year, due to high deductibles or no coverage at all.
More patients are aging, ill and need multidrug regimens, compounding costs
An increase in chronic illness means increased costs for patients on a population level. For the individual patient, managing a chronic illness can mean ongoing prescription costs and regular appointments with multiple providers. No amount of financial planning or preparation can prepare patients for the bills some chronic illnesses rack up.
This leaves individuals and families vulnerable to medical debt, bankruptcy and complete loss of retirement and savings.
A prevailing rise in chronic illness
There are more chronically ill patients today than ever before, and that increase requires more medications — which can compound out-of-pocket costs. Six in 10 adults in the U.S. have at least one chronic disease.Chronic Diseases in America, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022 Four in 10 have more.Chronic Diseases in America, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022 Each chronic illness may require multiple medications to treat. People living with cancer, for example, can take five or more medications, on average.Use of Prescription and Non-Prescription Medications and Supplements by Cancer Patients during Chemotherapy; Questionnaire Validation, Hanigan et. Al., 2008
Patients can’t afford therapies they need, which means they’re making difficult choices
Patients are sometimes forced to choose between paying for their medications or other basic needs. Some try to make both work by skipping or spacing out prescriptions. Each situation can lead to poorer health outcomes.
The Affordability Pipeline
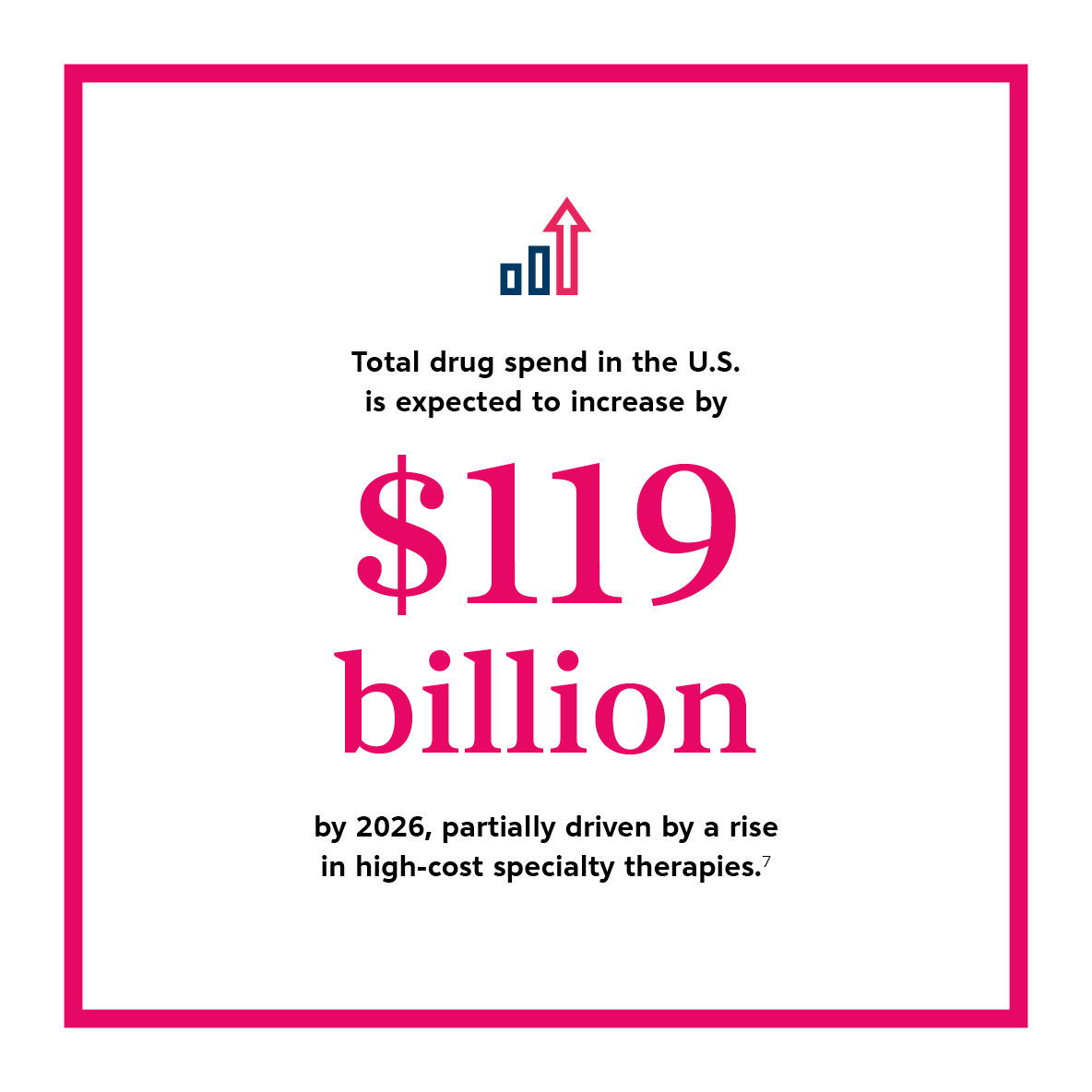
As drug spend rises, affordability becomes increasingly strained. Specialty therapies continue to be a dominant force in the pipeline. Oncology and autoimmune treatments are the biggest sectors driving pipeline growth.The Global Use of Medicines 2022, IQVIA, 2022 Specialty therapies saw an increased average cost of nearly 5% in 2020 for the top 180 drugs — more than three times the rate of general inflation for that same period and represent 53% of the overall pharmaceutical market spend.Rx Price Watch: Trends in Retail Prices of Specialty Prescription Drugs Widely Used by Older Americans, 2006 to 2020,The Use of Medicines in the U.S. Spending and Usage Trends and Outlook to 2025, IQVIA, 2021
Affordability Barriers
Payers’ strategies to shift more costs to patients continue to mutate around industry counterefforts — a huge impact to patient lives.
The rise of high-deductible health plans (HDHPs)
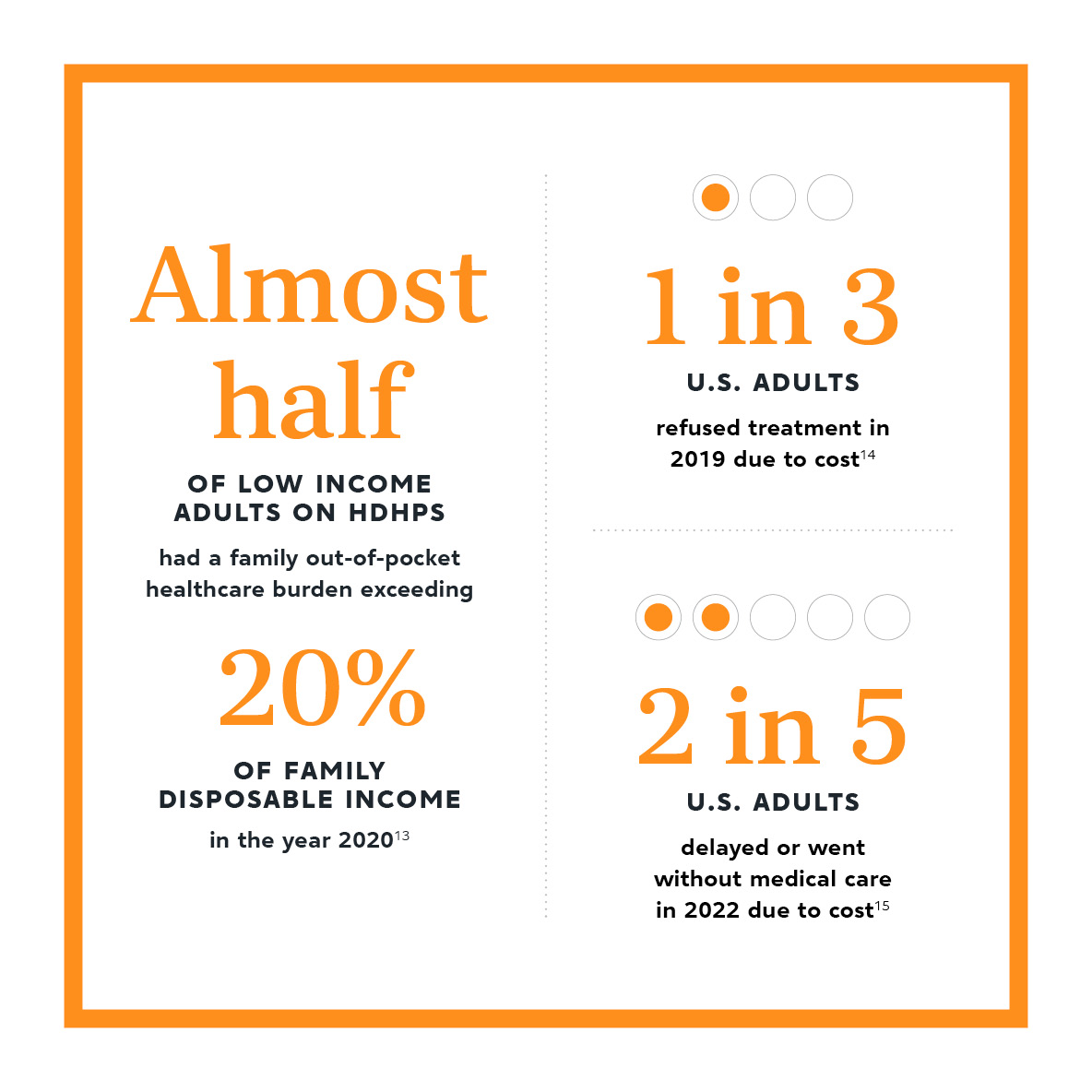
HDHPs were meant to save costs for employer-sponsored health plans by shifting costs away from the insurer and onto the patient. However, a 2020 study from the National Bureau of Economic Research found that while HDHPs can have a limited short-term impact on spending growth, the impacts were only statistically significant for prescription drugs, and the mitigation was only observed for the first year, after which spending increased again.How Does Cost-Sharing Impact Spending Growth and Cost-Effective Treatments? Evidence from Deductibles, Nationtal Bureau of Economic Research, 2020 This study follows a 2020 report from the American Medical Association (AMA) that found reductions in healthcare spending were simply the result of patients receiving less medical care.Help cut burdens of high-deductible health plans, American Medical Association, 2020
Especially under HDHPs, even if patients seek treatment and services covered under their health plan, they still face significant copayments, coinsurance, and medical bills before they meet their deductibles.High-Deductible Health Plans Continue to Grow in Popularity, but Are They Right for You?, Value Penguin, 2022 Ultimately, when patients are less proactive in seeking treatment and less adherent to recommended care, they’re more likely to face further complications and increase use of acute care services.High-Deductible Health Plans Continue to Grow in Popularity, but Are They Right for You?, Value Penguin, 2022
High deductibles, high costs
HDHPs can force cost-sharing onto patients by setting unattainable challenges.
It’s scary for patients to be stuck with a huge, unexpected cost, and it impacts their health, no matter what condition they have … Treatment these days is prevention.
DirectorHIV-AIDS Patient Advocacy Organization
What You Can Do
As patients’ share of medication costs increases, access to therapy is greatly affected.
With strategic support from industry partners, pharma manufacturers can work around these barriers to help their therapies succeed to achieve better health outcomes for patients.
Provider education and awareness
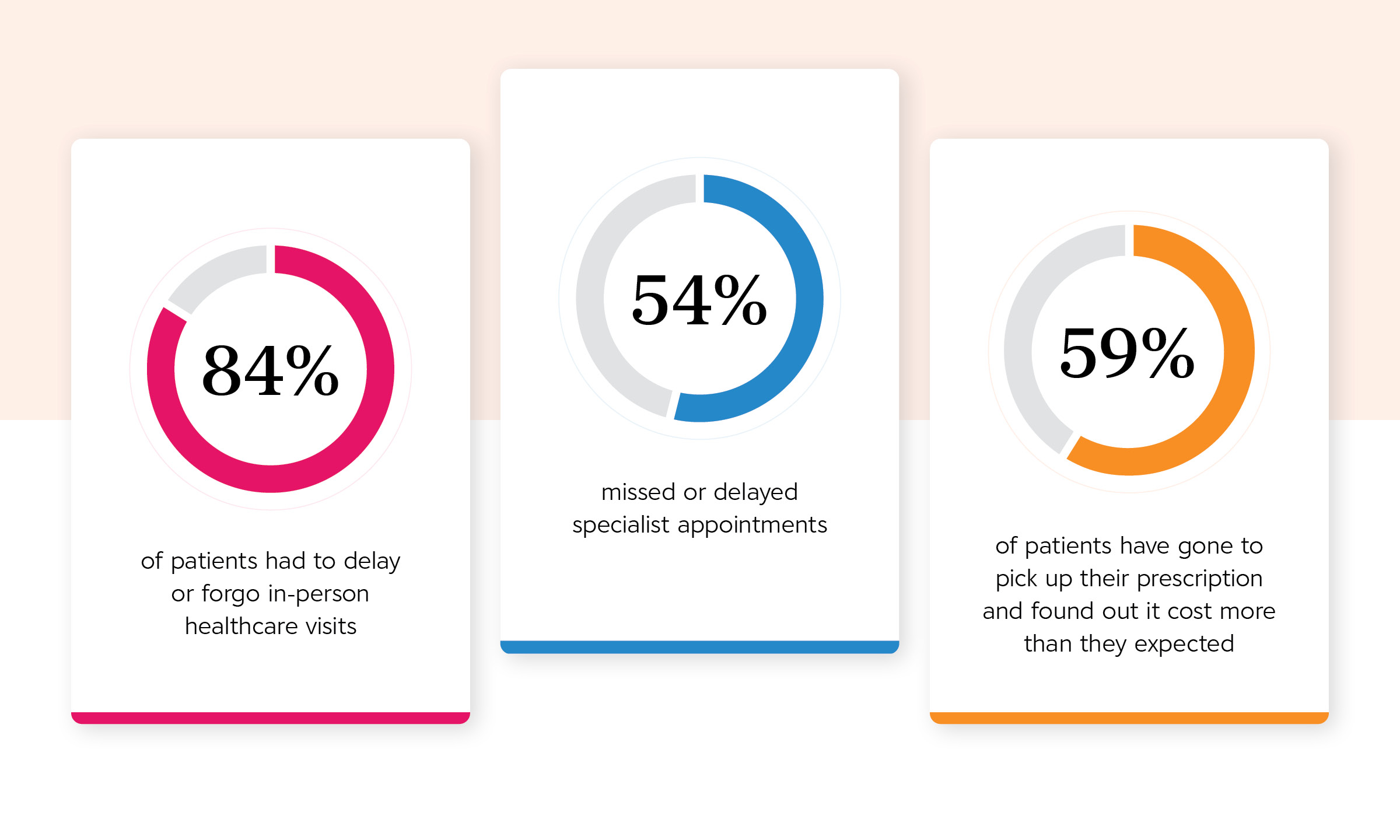
Lack of transparency in prescription affordability starts at the point of prescription. In 2022, 59% of patients found out a prescription cost more than they expected when they went to pick it up.CoverMyMeds Patient Survey, 2023 This led to abandonment in some cases, but most leaned on their provider or pharmacist for alternatives.CoverMyMeds Patient Survey, 2023 If a provider knows a patient can’t afford their medication, but isn’t aware of affordability options, they may choose a less preferred medication.
Pharma manufacturers can use data and network channels to communicate upstream to the providers and help them make a more informed selection at the point of prescription. Solutions that include this information can help providers stay up to date on formularies, prior authorization (PA) requirements and copay savings that may be available to the patient — at the point of prescribing. This information helps prescribers focus on making the best health decisions for their patients without having to sacrifice based on cost, making in-workflow education a crucial part of a launch and ongoing affordability strategy.
At the pharmacy
The point of dispensing is a crucial step in the patient journey. It’s often when they discover what their financial burden is, which their provider may not have discussed with them, and ask about potential side effects and other treatment directions.
It’s important to consider pharmacy in any copay strategy or patient assistance program, especially as 44% of patients in 2021 talked to their pharmacist about affordability options.CoverMyMeds Patient Survey, 2021 In some cases, pharmacists can become a patient’s primary point of contact regarding their prescriptions.
As clinicians, pharmacists often want to focus on patient care, with over three-fourths stating the most fulfilling parts of their jobs are counseling patients on their medications and conditions.CoverMyMeds Pharmacist Survey, 2021 However, their time is often taken up with the operational components of their role.CoverMyMeds Pharmacist Survey, 2021 Information sharing and streamlining can assist them in meeting patients’ needs.
Data that connects the dots between industry players helps get information upstream to inform the prescribing decision and downstream to help the patient and the pharmacist navigate cost complexities to get the patient onto a medication they can afford.
Payer partnerships
As the industry prepares for greater shifts into value-based systems, data and outcomes will be increasingly important for all stakeholders. Payers often hold vast amounts of data that could help pharma manufacturers address patients more effectively. Through data analysis and transparency, both parties can assess what interventions are most effective for patients and how to find the most effective — and therefore cost efficient — option for treating various conditions.Pharma-Payer Partnerships Seek to Prove Effectiveness of Care, AJMC, 2014 This data can also help pharma manufacturers understand benefit design and how to structure their affordability programs to impact the greatest amount of patients.
Solutions to enable patient access
A comprehensive affordability strategy will include patient-support services and solutions that encompass the entire patient journey, from point of prescription through long-term adherence. This strategy will also include educating and empowering the patient with better options, helping them through coverage barriers and providing financial support that will allow them to start or stay on therapy.
Comprehensive Affordability Solutions Across the Patient Journey
1. Better transparency empowers patients
- Real-time communications and updates keep patients informed and in control
- Safer, more accurate prescriptions protect patients from additional costs and wait times
- Cost transparency helps patients make financial decisions surrounding their health
2. Navigating coverage barriers may reduce time to therapy
- Simplifying PA can prevent unnecessary therapy delay
- Coverage support helps patients battle denials and adjudicate claims
- Bridge programs may help eligible patients initiate therapy sooner (sometimes for free) while awaiting approval from their payer or PBM
3. Providing financial relief can help patients stay on therapy
- Copay cards and cash discounts equip patients at the pharmacy
- Support for out-of-pocket costs helps patients manage HDHPs
- Free drug programs may help eligible patients access therapy when they couldn’t otherwise
Designing Your Affordability Program
Keeping patients at the center of affordability program design is crucial to overall success. Medication affordability can further impact access and adherence to therapies.
1. Strategic program design
Understand the potential impact of health plan design across various chronic and specialty therapy categories in a manner that becomes more intuitive over time and allows companies to provide smarter patient support.
Test program design by leveraging historic aggregated claims data to apply “what-if” scenarios and model how those factors will affect retention and budget.
Quantify claims impacted by copay programs and break down claims by program volumes, therapeutic category and financial impact.
2. Increased patient reach
- Design a launch strategy to ensure the program achieves optimal patient reach through providers and pharmacies.
- Integrate controls within the point-of-sale adjudication process by providing insight for patients into their financial responsibility at each transaction.
- Engage patients and boost awareness and education through timely, easy-to-use mobile enrollment that includes live agent, web and interactive voice response options.
3. Tailored support
Tailor copay strategies to meet the needs of various patient coverages, product life cycle and therapeutic area.
Reduce impact of claim denials and, by extension, prescription abandonment, by electronically connecting copay assistance programs with PA challenges.
Provide cohesive support across patient support solutions for connectivity across copay programs and hub programs.
The latest healthcare insights, floated right to your inbox.



